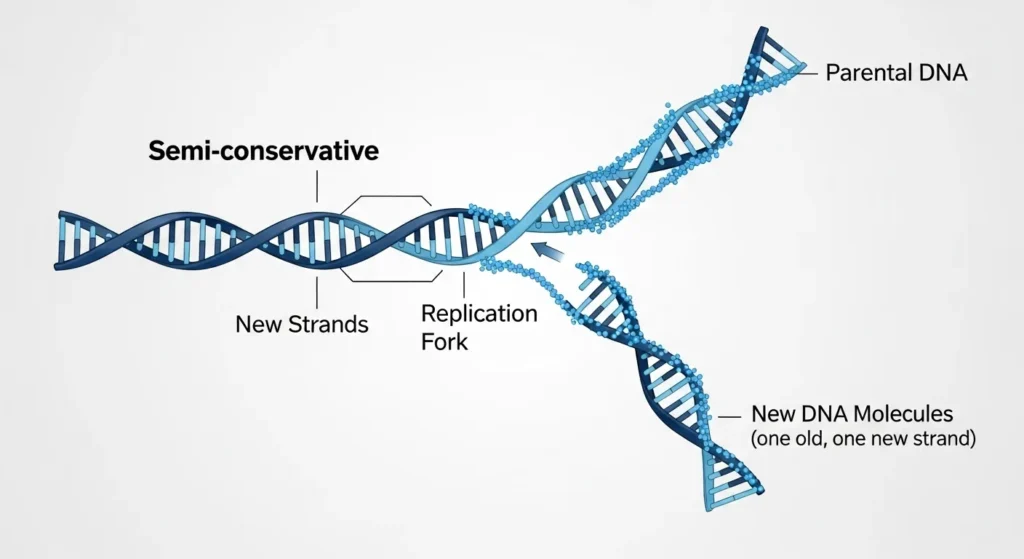
In DNA replication, semi conservative means that each new DNA molecule contains one original parental strand and one newly synthesized strand.
DNA replication is one of the most important biological processes because it allows cells to divide and pass genetic information to new cells. Without accurate replication, life as we know it would not be possible. One key concept students often encounter while learning about DNA replication is the term semi conservative.
At first, the phrase may sound complex, but the idea behind it is actually very logical and elegant. Understanding what semi conservative means in DNA replication helps explain how genetic information remains stable across generations while still allowing for growth and repair.
This article explains the meaning of semi conservative replication, its origin, how it works, why it is important, examples, comparisons with other replication models, alternate meanings, and answers to common questions.
Origin of the Term Semi Conservative Replication
The concept of semi conservative DNA replication was proposed shortly after the structure of DNA was discovered by Watson and Crick in 1953. Scientists hypothesized that DNA replication must follow a specific pattern to ensure accuracy.
The idea was later proven experimentally in 1958 by Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl. Their famous experiment used isotopes of nitrogen to show that each new DNA molecule contained one old strand and one new strand. This experiment became one of the most important proofs in molecular biology.
The term semi conservative reflects this process because half of the original DNA is conserved in each daughter molecule.
Popularity and Real World Usage
Semi conservative replication is a foundational concept taught in biology classes around the world. It is commonly discussed in high school biology, college level genetics, molecular biology, and medical studies.
Beyond education, this concept is essential in real world applications such as genetic research, cancer studies, DNA sequencing, and biotechnology. Understanding how DNA replicates accurately helps scientists study mutations, genetic disorders, and inheritance patterns.
How Semi Conservative DNA Replication Works
DNA replication begins when the double helix unwinds and the two strands separate. Each original strand then serves as a template for the creation of a new complementary strand.
Because DNA bases pair specifically, adenine pairs with thymine and cytosine pairs with guanine. Using this rule, the cell builds a new strand that matches the original template.
At the end of replication, two DNA molecules are formed. Each molecule contains one original strand and one newly formed strand. This is why the process is called semi conservative.
Why DNA Replication Is Called Semi Conservative
DNA replication is called semi conservative because it conserves one strand of the original DNA in each new molecule. The original DNA is not completely preserved as a whole, nor is it entirely replaced.
Instead, the genetic information is shared between old and new strands, ensuring accuracy while allowing replication to proceed efficiently. This balance between preservation and renewal is what makes the process reliable.
Simple Example to Understand Semi Conservative Replication
Imagine a zipper being pulled apart. Each side of the zipper represents one strand of DNA. When the zipper separates, each side helps create a new matching side.
After the process, you end up with two zippers. Each zipper has one original side and one new side. This simple analogy helps visualize how semi conservative replication works.
Comparison With Other DNA Replication Models
Before semi conservative replication was confirmed, scientists proposed other models.
Conservative replication suggested that the original DNA molecule stays intact and an entirely new copy is made. Dispersive replication suggested that original and new DNA segments are mixed throughout each strand.
Experimental evidence showed that neither of these models was correct. Semi conservative replication accurately explained how DNA copies itself while maintaining genetic stability.
Importance of Semi Conservative DNA Replication
Semi conservative replication ensures genetic consistency across cell divisions. It reduces errors, allows DNA repair mechanisms to function effectively, and supports evolution by permitting controlled mutations.
This process is vital for growth, tissue repair, reproduction, and inheritance. Without semi conservative replication, organisms would not be able to survive or evolve.
Alternate Meanings of Semi Conservative
Outside of biology, the term semi conservative can describe something that partially preserves original features while allowing some change. However, in scientific contexts, semi conservative is most commonly associated with DNA replication.
In genetics, the term has a very specific and well defined meaning.
Polite and Clear Alternatives for Explaining Semi Conservative Replication
Instead of using technical language, educators sometimes explain semi conservative replication as
each new DNA has one old strand and one new strand
half of the original DNA is kept in each copy
DNA copies itself using existing strands as templates
These explanations make the concept easier for beginners.
FAQs
What does semi conservative mean in simple terms?
It means each new DNA molecule has one old strand and one new strand.
Who proved semi conservative DNA replication?
Meselson and Stahl proved it through an experiment in 1958.
Why is DNA replication not fully conservative?
Because the original DNA does not stay completely intact after replication.
Is semi conservative replication accurate?
Yes, it is highly accurate and supported by strong experimental evidence.
Does semi conservative replication occur in all organisms?
Yes, it occurs in all living organisms that use DNA as genetic material.
What would happen without semi conservative replication?
Genetic errors would increase, and inheritance would become unstable.
Is RNA replication semi conservative?
No, RNA replication follows different mechanisms depending on the organism.
Why is semi conservative replication important in medicine?
It helps scientists understand mutations, cancer, and genetic diseases.
Conclusion
Understanding what semi conservative means in DNA replication is essential for learning how genetic information is preserved and passed on. Semi conservative replication ensures that each new DNA molecule contains one original strand and one newly synthesized strand.
This process maintains accuracy, supports life, and allows organisms to grow and reproduce. From basic biology education to advanced medical research, the concept of semi conservative replication remains a cornerstone of modern science.
See Also More:
- What Does RA Mean in Medical Terms ? Full Explained 2026
- What Does Third Base Mean in a Relationship in Dating Culture 2026